The new version of the internet will be based on a decentralised ledger technology, commonly known as blockchain technology…
The Agricultural Revolution is considered one of the causes of the Industrial Revolution because improved agricultural productivity freed up workers to work in other sectors of the economy. In contrast, per-capita food supply in Europe was stagnant or declining and did not improve in some parts of Europe until the late 18th century.
Industrial technologies that affected farming included the seed drill, the Dutch plough, which contained iron parts, and the threshing machine. Machine tools and metalworking techniques developed during the Industrial Revolution eventually resulted in precision manufacturing techniques in the late 19th century for mass-producing agricultural equipment, such as reapers, binders, and combine harvesters.
The cliff notes on the history of Industries:
- Industry 1.0 = mechanization & steam power;
- Industry 2.0 = assembly line;
- Industry 3.0 = computerization & automation;
- Industry 4.0 = digital transformation. It is simply the physical world becoming digital.

Innovation – the introduction of something new and valuable
The world is fraught with problems that are difficult to solve, but that will continue to demand a solution. Rather, far-sighted, creative ideas and innovative solutions are required. A degree of innovation is key in the current volatile and uncertain business environment. Organizations who understand this and can seek out and act upon the opportunities and possibilities for change through innovation will not only survive; they will successfully compete and even flourish.
Innovation is explained as to “make changes in something established, especially by introducing new methods, ideas, or products” – the Oxford English dictionary. The tendency is to see three distinct approaches to innovation in businesses today: incremental innovation, breakthrough innovation and radical innovation. These can be mapped against two axes — business model newness and technology newness.

Web 3.0 Explained
I have already published a first article about web 3.0, but let’s go a little further.
To discuss the definition of Web 3.0, it is the third iteration of the internet that would be able to think like us. Like, it would not only able to understand the meaning of the words but also the context, sense and emotions behind them.
The new version of the internet will be based on a decentralised ledger technology, commonly known as blockchain technology. The technology will bring the aspect of decentralization into the system and allow the user to have control over their data. This is stark opposite to the current version of the internet, known as Web 2.0, wherein the data is centralized and controlled by a few tech giants.
Features of Web 3.0
Decentralization
This is the core feature of Web 3.0. While today in Web 2.0 the data is stored at a particular location or server that is the property of a certain organization. This leaves the control of that data in the hands of that organization, which can use it for profiteering.
Thus, jeopardizing the privacy of many users. This is one of the main drawbacks of Web 2.0 that Web 3.0 seeks to do away with.
Since Web 3.0 is based on blockchain, a decentralized ledger technology, which stores data in multiple locations, it will also result in distributed data storage simultaneously. This will give the user complete authority over their data and protect their privacy.
Trustless & Permissionless
In the context of Web 3.0, being trustless is a positive word. This is because, the network will allow the user to interact with it directly without requiring any intermediary. Thus, they don’t need to entrust anyone with their data before putting it on the network. They can do it on their own and keep it safe with the help of unbreakable blockchain technology.
Similarly, the users do not need to acquire permission from anyone before interacting with this network. This makes them permissionless.
Semantic Web
This is one of the most prominent improvements in Web 3.0 over the preceding versions. It would not only work based on the keywords the user puts in but also understands the underlying context.
Thus, it produces the results according to the sense of the search and not just the keywords as it’s being done in the current version i.e. Web 2.0. It understands the difference between Jaguar the car and Jaguar the animal.
Artificial Intelligence
The next big improvement is the utilization of Artificial Intelligence. With the help of AI, Web 3.0 would be able to understand data as we do. And this will change how we interact with the digital world, given that it will also include Natural Language Processing (NLP).
Thus, the AI in Web 3.0 would be able to identify ambiguity or abnormality in data. Moreover, with the help of Machine Learning, it will keep on improving itself and give better results everytime.
Spatial Web
Web 3.0 will also deal extensively with 3D graphics, that is why many futurists also call it Spatial Web. This will enhance the immersive experience of the user to the manifold, for example, the user would be able to see the product on an e-commerce website in more clearer manner.
Similarly, Museums would be able to give an online tour or showcase their distinguished artifacts to attract visitors. Likewise, it can be utilized in healthcare, education, real-estate you name it.
Hence, the opportunities are boundless with the amazing 3D experience Web 3.0 will be able to offer to blur the line between the physical and the digital worlds (e.g. Metaverse).
Connectivity
The connectivity will be in two forms. The first is the connectivity between the information and the second is connectivity between machines for example Internet of Things (IoT).
The first form of connectivity will be a result of AI. The reason, since this information system will itself understand the information, it will be able to juxtapose related information to present more productive results.
The second form of connectivity will be caused by two factors:
- Enabling technologies like Cloud Computing, Robotics, Big Data
- Mushrooming on Automated machines that can connect to the internet,
These two factors will transform the interaction between humans and machines. And the common thread that will connect all these developments will be Web 3.0.
This will take the connectivity aspect of Web 3.0 to unprecedented levels. And usher in the high-tech future. And this takes us to another feature.
Ubiquity/Omnipresence
This will be a result of a higher extent of connectivity in Web 3.0 making it ubiquitous. Although, Web 2.0 is ubiquitous up to a limited extent for example only certain sites allow you to access your data from anywhere in the world. This data is solely controlled by the organization managing the website.
Web 3.0 will take this feature to another level. The data will be accessible from around the world. Not only the data will be accessible to the user from anywhere in the world. The user would be the sole owner of their data.

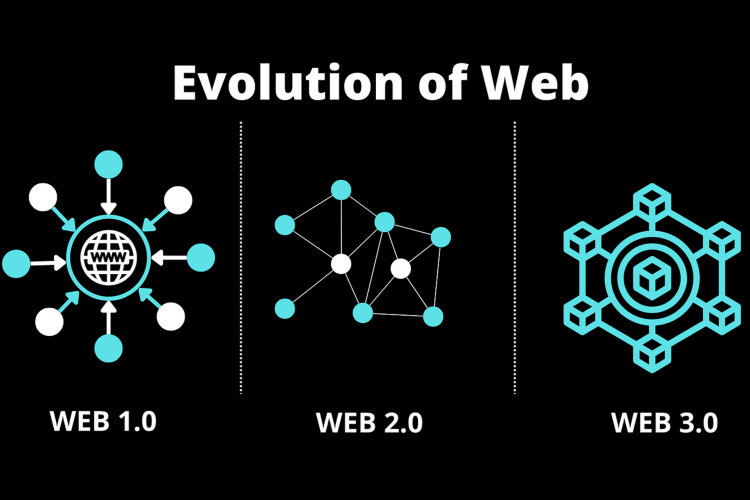
Comparison between Web 1.0 vs Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0
Web 1.0 = the read-only Internet
It is called Static web because there was very limited interaction between the internet and the user. The information was very provided in a very straightforward and bland and access to it was very limited.
Also, the search engine only came into existence after 1995, which made email and access to real-time information possible. However, it was a time when few created the content for many (1980s–early 2000s). And this got changed in Web 2.0.
Web 2.0 = read-write Internet
It was a great shift from its previous version. Not only was it better when it came to interactivity and social connectivity. It allowed the user to generate content and let it spread across the internet to other millions or even billions of users. That is why it is also called the Social Web.
The most noticeable development was the advent of social networking and interactive applications. This facilitated the emergence of tech giants like Facebook, Google, Twitter, Youtube, etc. These giants gradually attained dominance on the internet by controlling its access and usage of the data over it.
Further, its growth got fueled by technological advancements like mobile phones and open source software like Android. These open-source software led to the development of millions of mobile-based software applications that expanded the utility of the internet to exponential levels (early 2000s–2020).
Web 3.0 = read-write-own Internet
Compared to the above two versions of the internet, Web 3.0 is based on the principles of decentralization, directness, privacy protection and permissionless access, and will offer the obvious purpose of greater utility.
Thus, it will give the user more authority over their data. This will curb the data usage of the users without their permission which is the most talked-about disadvantage of Web 2.0.
As envisaged, it will take the bottom-up approach in which the users will guide the direction it would take. Moreover, the features that we discussed above like Semantic Web, Artificial Intelligence, Three-dimensional graphics, etc will offer even more utility in Web 3.0 (2020–today).
Advantages of Web 3.0
Ownership of Data
Under the Web 3.0 setting, the user gains ownership of their data and the privacy is protected by encryption of the data through blockchain technology. Therefore, this data can only be utilized by any third party after getting permission from the user on a need or case-by-case basis.
Ubiquitous Information Access
Web 3.0 enables ubiquitous information access, which is quite limited in Web 2.0. This will be made possible with the help of smartphone applications and cloud-based technologies. While in Web 2.0 users have to rely on an intermediary to access their own data, this will not be the case in Web 3.0 where there would be no intermediary.
Democratization of the Web
Web 3.0 provides democratization of the web as no central authority can dictate the access to its services, and neither can anyone stop its operation. It will execute the same functions in all circumstances thanks to the architecture that is based upon smart contracts (=execution of a computer program that may include special conditions or checks).
A data center is said to be hyperscale when it uses these techniques to host and operate several thousand servers. In computing, hyperscale is the ability of an architecture to scale appropriately as increased demand is added to the system. Examples of hyperscalers are Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google GCP, Alibaba AliCloud, IBM, and Oracle.
Web 3.0 is based on blockchain protocols that support online privacy, self-sovereign identity, and property rights to digital assets.
Database and Blockchain both record transactions, but the database is centralized and has a single point of failure. In contrast, the Blockchain is decentralized and distributed on multiple nodes (computers) across the network.
- Databases are owned by a central authority, a company, or a government institution, which controls access by granting different roles to different users.
- Whereas Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network where each node can connect with every other node, and blocks in a chain are connected using a secure cryptographic protocol.
It may be too late to replicate hyperscalers, but it is not too late to achieve technological sovereignty in some critical technology areas.
Ursula von der Leyen, President of the European Commission – Excerpt from Political guidelines for the next European Commission 2019-2024